What is Public Key Cryptography?
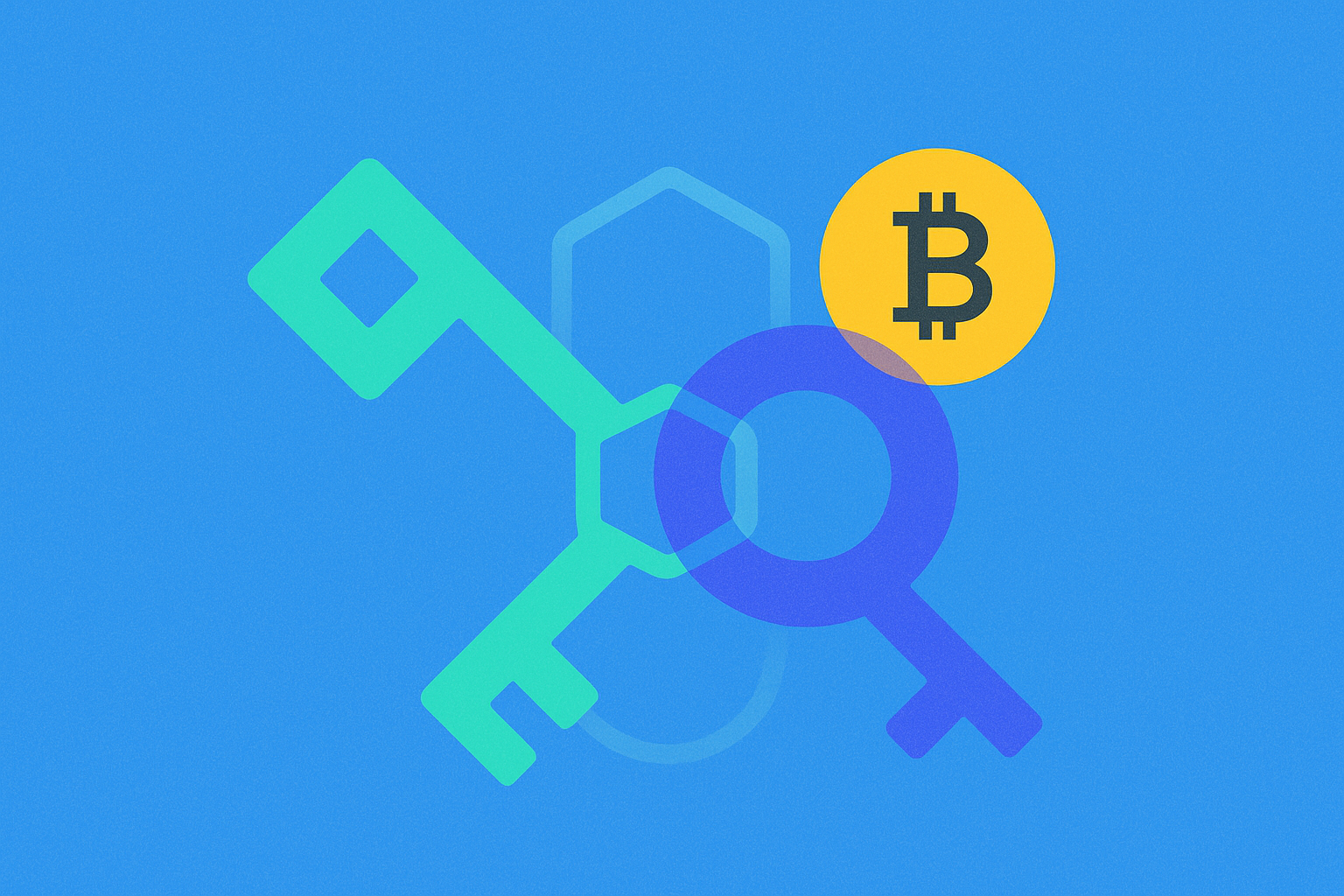


How Public Key Cryptography Works
Public key cryptography, also called asymmetric cryptography, is a system that uses a pair of keys—public and private—unlike symmetric cryptography, which relies on a single key. Using key pairs gives public key cryptography unique attributes that address challenges found in other cryptographic methods. This encryption method is now a cornerstone of modern computer security and is vital to the expanding cryptocurrency ecosystem.
In a public key infrastructure, the sender encrypts information with the recipient’s public key, and the recipient decrypts it using their private key. Since the keys are distinct, the public key can be shared openly without jeopardizing the private key’s security. Each asymmetric key pair is unique, ensuring that only the holder of the matching private key can decrypt messages encrypted with its public key.
Asymmetric algorithms generate mathematically linked key pairs, which is why these keys are much longer than those used in symmetric encryption. Key lengths typically range from 1,024 to 2,048 bits, making it extremely difficult to derive the private key from the public key. One of the most widely used asymmetric cryptography algorithms is RSA. In RSA, keys are generated using a modulus produced by multiplying two large prime numbers. The modulus generates two keys: a public key for sharing and a private key that must remain confidential. First described in 1977 by Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman, RSA remains a core element of public key cryptography even today.
PKC as an Encryption Tool
Public key cryptography solves a major issue with symmetric algorithms: securely communicating the key used for both encryption and decryption. Sending this key over an unsecured channel can expose it to third parties, allowing them to read any messages encrypted with it. Methods like the Diffie-Hellman-Merkle key exchange attempt to address this, but remain susceptible to certain attacks. In contrast, public key cryptography allows the encryption key to be shared safely over any connection. As a result, asymmetric algorithms provide stronger protection than symmetric ones.
Role in Digital Signature Generation
Asymmetric cryptography is also essential for data authentication through digital signatures. A digital signature is essentially a hash generated from message data. When the message is sent, recipients can verify the signature using the sender’s public key, confirming the message’s origin and ensuring it hasn’t been altered. Sometimes, digital signatures and encryption are used together, with the hash itself encrypted as part of the message. However, not every digital signature scheme relies on cryptographic techniques.
Limitations
While public key cryptography enhances computer security and message integrity, PKC does have noteworthy limitations. The complex mathematics involved in encryption and decryption make asymmetric algorithms relatively slow when processing large datasets. This approach also relies on keeping the private key secret. If a private key is exposed or shared, all data encrypted with the associated public key becomes vulnerable. Additionally, if users lose their private keys, they permanently lose access to the encrypted information.
Public Key Cryptography Applications
Modern computer systems use public key cryptography to secure sensitive information. For example, emails can be encrypted using public key methods to protect their contents. The SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol, which secures web connections, also relies on asymmetric encryption. Public key systems have even been considered for secure electronic voting, potentially allowing voters to cast ballots from home.
Public key cryptography is especially critical in blockchain and cryptocurrency environments. Creating a new crypto wallet generates a key pair: a public key and a private key. The public address, derived from the public key, can be safely shared with others. The private key, however, is required to create digital signatures and validate transactions, making it essential to keep private. Once a transaction is verified by checking the hash in the digital signature, it is added to the blockchain ledger. This signature verification process ensures that only the private key holder of the appropriate crypto wallet can authorize outgoing transactions.
Notably, the asymmetric ciphers used in cryptocurrencies differ from those in traditional computer security. Many blockchain systems implement a specialized scheme known as the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) to verify transactions securely and efficiently.
From securing computer systems to validating cryptocurrency transactions, public key cryptography is vital to protecting today’s digital infrastructure. By leveraging paired public and private keys, asymmetric encryption addresses core vulnerabilities inherent in symmetric ciphers. Although PKC has a long history, it continues to evolve, especially across blockchain and cryptocurrency industries.
FAQ
What is public key cryptography and how does it work?
Public key cryptography employs a key pair: a public key to encrypt data and a private key to decrypt it. This asymmetric approach is foundational for secure digital transactions and protects wallets and assets in Web3 environments.
What’s the difference between public key cryptography and symmetric key cryptography?
Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. Public key cryptography uses a pair: the public key encrypts, and the private key decrypts, delivering stronger communication security.
What are the real-world applications of public key cryptography?
Public key cryptography secures email, generates digital signatures, authenticates users, and underpins secure online transactions using protocols like SSL/TLS—making it essential for digital trust.
How does public key cryptography ensure secure data transmission?
Public key cryptography secures data by using a key pair: the public key encrypts information, and only the matching private key can decrypt it. This mechanism protects both confidentiality and authenticity of transmitted data.
What are public and private keys, and how do they work together?
Public and private keys form a cryptographic pair. The public key is used to encrypt data and is openly shared, while the private key decrypts and remains confidential. Together, they provide security, authenticity, and privacy for blockchain transactions.
Understanding On-Chain: A Guide to On-Chain Transactions
Cookie Là Gì?
Understanding Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption Techniques

How to Find Your Crypto Address (Across All Wallets and Blockchains)

Crypto Wallets Explained

Gate Wallet: A Secure Multi-Chain Solution for Web3 in 2025

How does XRP's market share compare to SWIFT and Solana in cross-border payments?
What Are Bitcoin Stamps?

What is the difference between PIEVERSE and Chainlink: competitive analysis of Web3 infrastructure tokens

How do exchange inflows and outflows impact cryptocurrency market sentiment and capital flow?
How active is crypto community and ecosystem in 2026: Twitter followers, developer contributions, and DApp growth analysis







